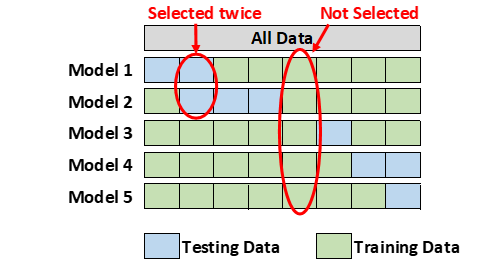
2.6 Monte Carlo Cross-Validation
Monte Carlo cross-validation creates multiple random splits of the data into training and testing sets. For each split, the model is fit to the training data, and predictive accuracy is assessed using the testing data. The results are then averaged over the splits. The disadvantage of this method is that some observations may never be selected in the testing subsample, whereas others may overlap, i.e., be selected more than once. (Lever 2016)